Problem
曼哈顿最小生成树
TimeLimit:10Sec
MemoryLimit:256MB
Description
平面坐标系xOy内,给定n个顶点V=(x,y)。对于顶点u,v,u与v之间的距离d定义为∣xu−xv∣+∣yu−yv∣。你的任务是求出这n个顶点的最小生成树。
第一行一个正整数n,表示定点个数。
接下来n行每行两个正整数x,y,描述一个顶点。
Output
只有一行,为最小生成树的边的距离和。
Sample Output
HINT
对于100%的数据,n≤5×104,0≤x,y≤105。
标签:树状数组 MST
Solution
MMST裸题。
对于曼哈顿最小生成树,直接建边肯定是不行的,考虑优化建边,去掉一些一定不会在MST中的边。
考虑一个点A(x1,y1),以A为中心将整个图分为8个部分。
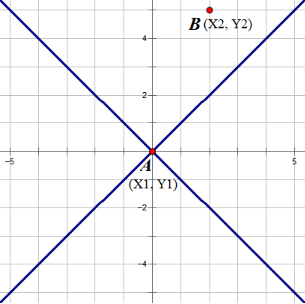
对于一个在右上角的点B(x2,y2),一定有x2−x1<y2−y1且x2>x1,若其使x2+y2−x1−y1最小,则所有在右上角的点的曼哈顿距离都没有A→B小。因此在A右上角的所有点中,只连AB即可。同理在A周围的八个方向中,每个方向只需连曼哈顿距离最小的点。
对于如何寻找这样的点,拿找右上角的最近点做例子:
最近的点B(x2,y2)一定使x2+y2−x1−y1最小,即使x2+y2最小。同时要满足x2−x1<y2−y1和x2>x1,即满足x2−y2<x1−y1且x2>x1。可以发现这就是以x为第一维,x−y为第二维做偏序,找到符合的位置中的最小值,用排序+树状数组维护。
这样我们就可以连每个点到其右上角的最近点的边了。考虑到边可以每次都连双向,因此每个点只用枚举一半即可。这里默认向y坐标比当前点大的点连边。其实是可以把每种情况都转化为右上角的。
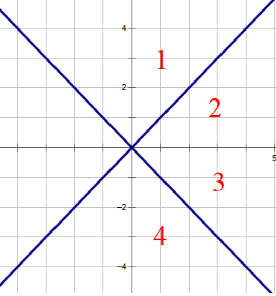
一开始的时候,我们总共需要考虑的是下图区域1,2,3,4中的最近点。第一次连边将1中的最近点连边。
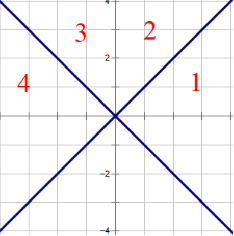
接下来将每个点的x,y坐标互换,即关于直线y=x对称,可以得到下图。第二次连边将2中的最近点连边。
然后将每个点的x坐标取反,即可得到下图。这时第三次连边将3中的最近点连边。
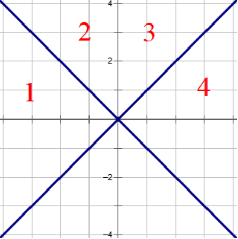
最后再次互换每个点的x,y坐标,得到下图。第四次连边将4中的最近点连边。
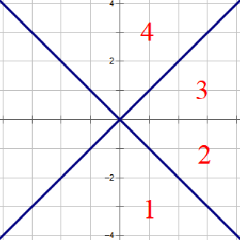
由此,我们可以不改回原值就将8个方向连边。
建图后,直接跑Kruskal或Prim即可。
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define MAX_N 100000
#define INF 4020010910LL
using namespace std;
typedef long long lnt;
template <class T> inline void read(T &x) {
x = 0; int c = getchar(), f = 1;
for (; !isdigit(c); c = getchar()) if (c == 45) f = -1;
for (; isdigit(c); c = getchar()) (x *= 10) += f*(c-'0');
}
int n, cnt, fa[MAX_N+5];
lnt tr[MAX_N+5]; int mi[MAX_N+5];
struct edge {int u, v; lnt c;} E[(MAX_N<<2)+5];
struct P {int id; lnt x, y;} p[MAX_N+5], q[MAX_N+5];
bool cmpe (const edge &a, const edge &b) {return a.c < b.c;}
bool cmpp (const P &a, const P &b) {return a.x == b.x ? a.y < b.y : a.x < b.x;}
lnt dist(int u, int v) {return abs(q[u].x-q[v].x)+abs(q[u].y-q[v].y);}
void addedge(int u, int v) {E[++cnt] = (edge){u, v, dist(u, v)};}
int getf(int x) {return fa[x] == x ? x : fa[x] = getf(fa[x]);}
void modify(int pos, lnt x, int id) {
for (; pos; pos -= pos&-pos)
if (tr[pos] > x) tr[pos] = x, mi[pos] = id;
}
int query(int pos) {
int ret = -1; lnt mc = INF;
for (; pos <= n; pos += pos&-pos)
if (tr[pos] < mc) mc = tr[pos], ret = mi[pos];
return ret;
}
void build() {
int a[MAX_N+5], b[MAX_N+5], m; sort(p+1, p+n+1, cmpp);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = b[i] = p[i].y-p[i].x;
sort(b+1, b+n+1), m = (int)(unique(b+1, b+n+1)-b-1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) tr[i] = INF;
memset(mi, -1, sizeof mi);
for (int i = n, rk, mp; i; i--) {
rk = (int)(lower_bound(b+1, b+m+1, a[i])-b);
mp = query(rk); if (~mp) addedge(p[i].id, mp);
modify(rk, p[i].x+p[i].y, p[i].id);
}
}
lnt MST() {
sort(E+1, E+cnt+1, cmpe); lnt ret = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) fa[i] = i;
for (int i = 1, u, v; i <= cnt; i++) {
u = getf(E[i].u), v = getf(E[i].v);
if (u^v) fa[u] = v, ret += E[i].c;
}
return ret;
}
int main() {
read(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
p[i].id = i, read(p[i].x), read(p[i].y), q[i] = p[i];
build(); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) swap(p[i].x, p[i].y);
build(); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) p[i].x *= -1;
build(); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) swap(p[i].x, p[i].y);
build(); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) p[i].y *= -1;
return printf("%lld\n", MST()), 0;
}
|